A compressed air dryer (a.k.a air dryers) removes moisture from compressed air systems. Moisture can cause corrosion, damage tools, and reduce efficiency. By eliminating water vapor, air dryers improve the longevity and performance of pneumatic equipment. But first of all let's look at why we need air dryers shortly.
Why Do We Need Compressed Air Dryers?
Compressed air dryers are crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of pneumatic systems. They remove moisture from compressed air, preventing various operational issues.
The Importance of Removing Moisture
Moisture in compressed air can cause significant damage. It leads to corrosion inside pipes, valves, and other components. This corrosion reduces the lifespan of equipment and increases maintenance costs. Removing moisture ensures that tools operate efficiently without interruptions or breakdowns.
Types of Compressed Air Dryers
Selecting the right compressed air dryer is crucial for maintaining pneumatic system efficiency and longevity. Let's dive into different type of air dryers.
Refrigerated Air Dryers
Refrigerated air dryers cool compressed air to remove moisture. These dryers use a refrigeration system to lower the temperature, causing water vapor to condense. They are ideal for general applications where dew points around 35-40°F are sufficient, such as in manufacturing and automotive industries. Two main types exist: cycling and non-cycling refrigerated dryers. Cycling models save energy by turning off during low demand periods, whereas non-cycling models maintain consistent operation regardless of load.
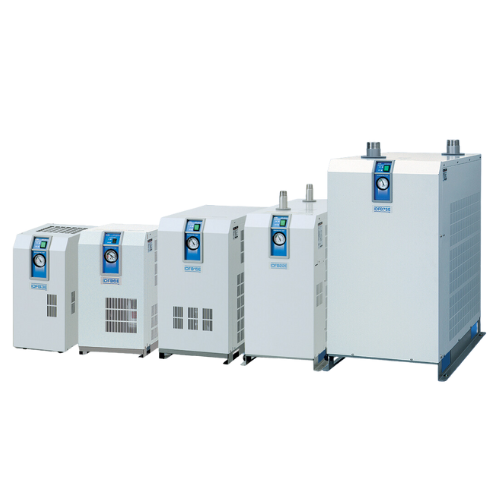

Desiccant Air Dryers
Desiccant air dryers utilize desiccant materials like silica gel or activated alumina to absorb moisture from compressed air. These dryers achieve very low dew points, often reaching -40°F or lower, making them suitable for environments requiring ultra-dry air, such as pharmaceutical manufacturing or electronics production. There are two primary types: heatless regenerative and heated regenerative desiccant dryers. Heatless models regenerate desiccant using a small portion of dried compressed air; heated models use internal or external heaters to accomplish regeneration more efficiently.

Membrane Air Dryers
Membrane air dryers employ selective permeation through a membrane material to separate moisture from compressed air. They offer simple installation and maintenance with no moving parts and minimal energy consumption. Membrane dryers suit applications needing moderate dew points (around 40-50°F) like laboratories or paint spraying operations where contamination-sensitive processes occur.

Deliquescent Air Dryers
Deliquescent air dryers use hygroscopic materials that dissolve gradually as they absorb moisture from the incoming compressed air stream. They provide reliable performance without electricity or complex controls, making them cost-effective solutions for remote locations or temporary setups in industries like construction or mining.
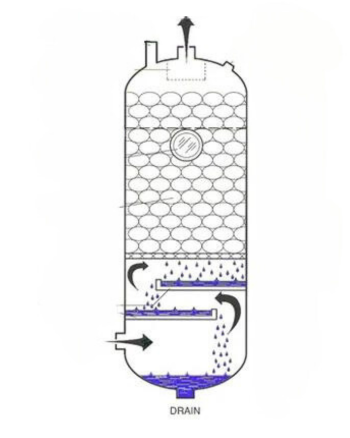
Each type of dryer offers unique benefits suited to different industrial needs, ensuring efficient operation of pneumatic systems across diverse environments.
| Dryer Type | Use | Method | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerated Dryers | General-purpose applications | Cools air to condense and remove moisture | Factory floor equipment |
| Desiccant Dryers | Ultra-dry air environments | Uses desiccant to absorb moisture | Pharmaceutical manufacturing |
| Membrane Dryers | Low dew points without power sources | Membrane technology separates water vapor | Paint spraying operations |
| Deliquescent Dryers | Remote locations without power | Hygroscopic salts absorb moisture | Oil drilling rigs |
| Heatless Regenerative Desiccant Dryers | Continuous drying with minimal energy | Alternates between drying and regenerating | High-demand industrial processes |
Application Specific Recommendations
Different industries benefit from specific types of air dryers:
- Laboratories and Medical Equipment: Membrane air dryers are ideal due to their compact size, quiet operation, and sufficient drying capacity for sensitive instruments.
- Food and Beverage Industry: Use refrigerated or membrane dryers to maintain hygiene standards without compromising moisture control.
- Paint Spraying Applications: Choose desiccant or membrane air dryers for achieving low dew points essential for preventing paint defects caused by moisture.
- General Manufacturing: Refrigerated air dryers provide an economical solution for moderate drying needs in various manufacturing processes.
By understanding these considerations, we can optimize our selection process to ensure peak efficiency across different applications.
Choosing the right air dryer is vital for maintaining efficient and effective pneumatic systems. Each type of air dryer offers unique benefits and considerations. By understanding specific needs like dew point requirements, flow rate, and energy efficiency, you can make informed decisions to ensure optimal performance across various applications.
As an authorized SMC distributor, Proax offers expert guidance and a wide range of SMC air dryers to help you find the perfect solution tailored to your specific compressed air system requirements. Contact us today.