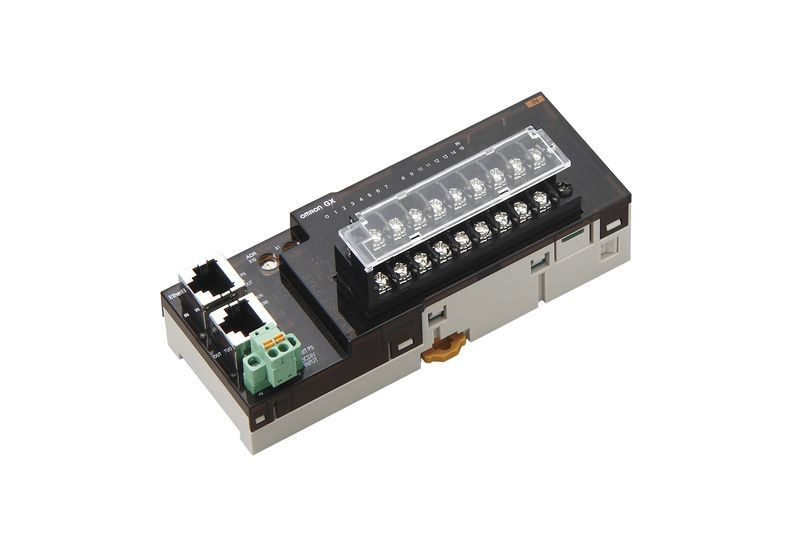
Ethernet switches
An Ethernet switch is a network device that connects multiple devices within a Local Area Network (LAN), enabling them to communicate efficiently. Discover our range of Ethernet switches designed for industrial applications, featuring various port configurations, mounting types, and connection options. Our switches ensure reliable data transfer and robust performance in demanding environments.
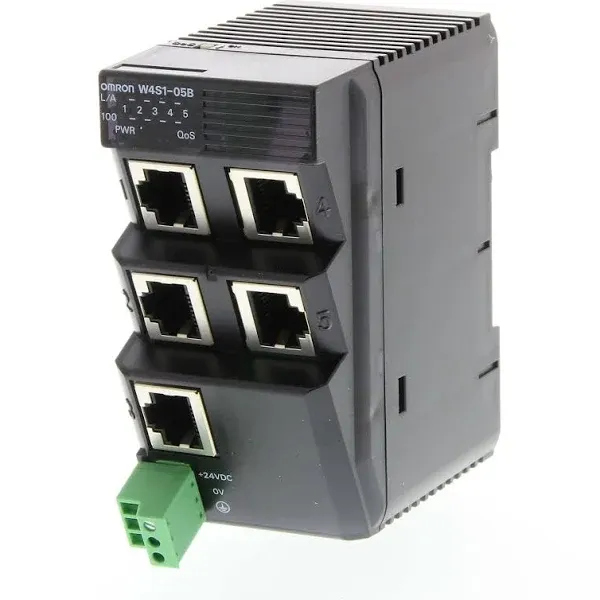

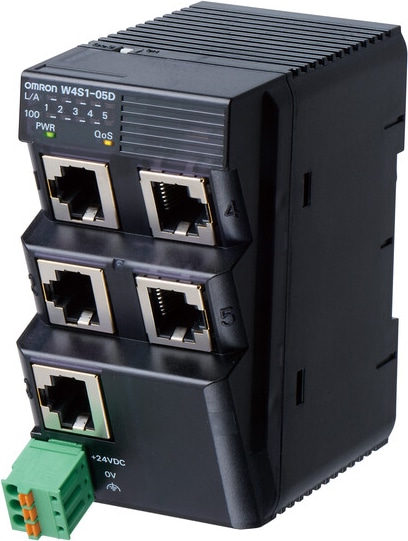
Omron W4S1 Ethernet Switch
- Superior Reliability: Unmanaged switches with no software settings, ensuring consistent control data performance on an Ethernet/IP network.
- Factory Automation: Ideal for environments with PLCs and robots, featuring simple DIN track mounting and optimized cable mounting angles.
- Enhanced Network Reliability: Includes failure and broadcast storm detection, with immediate notifications via contact outputs and LED indicators.
- Product Variation: Available in 3-port and 5-port models for various applications.
- Quality of Service (QoS): High-speed control data delivery with packet prioritization control, enabled by a DIP switch setting.
Ethernet Switch FAQs
An Ethernet switch is used to connect multiple devices within a LAN, allowing them to communicate efficiently. It manages and directs data traffic to ensure smooth and reliable communication between devices.
An Ethernet switch is generally better than a splitter. While a splitter divides a single connection into two, it doesn't manage data traffic. A switch, on the other hand, directs data packets to their correct destination, improving network performance and reducing collisions.
Yes, Ethernet switches are worth it, especially for networks with multiple devices. They improve network efficiency, manage data traffic effectively, and provide faster, more reliable connections compared to unmanaged splitters.
An Ethernet switch can be faster than a router for internal network traffic because it is designed to handle data transfers within the network efficiently. However, routers are necessary for connecting to external networks (e.g., the internet) and managing traffic between different networks.