Contactors
Contactors are electrically controlled switches used for switching an electrical power circuit. Explore our range of contactors, including the Series CA8, CA7, CA9, and CDP2, which offer high performance and reliability. With various control circuit voltages available, our contactors cater to different system requirements. Additionally, options with multiple auxiliary contacts ensure versatile application. Discover the perfect contactor for your needs with robust and efficient solutions.
Series
AF 3-pole Contactors

AF 4-pole Contactors

Contactors for Capacitor Switching

Contactors for DC switching

AFS contactors for safety applications

Installation Contactors

Definite Purpose Contactors

CR160 Lighting Contactors

CR360L Lighting Contactors

CR460 Lighting Contactors

Series CA7 Contactors


Series CA8 Contactors


Series CA9 Contactors


Series CDP2 Contactors

J7KC Magnetic Contactor

J7KCA Auxiliary Contact Relay
J7KCR Reversing Magnetic Contactor
Related Categories
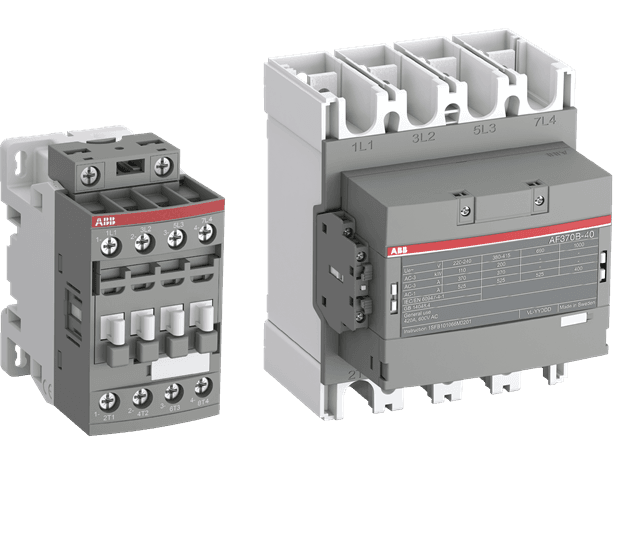
AF 3-Pole Contactors
- Secure Uptime: Overbridge voltage drops and sags with AF technology.
- Optimize Stocks: Fewer product variants reduce logistics and administration costs.
- Global Support: Use the same products worldwide with the 100–250 V AC/DC coil.
- Fast Wiring: Push-in Spring terminals for quick and reliable connections.
- Energy Efficiency: Reduce coil energy consumption by 80%.
Contactors FAQs
A contactor is an electrically controlled switch used for switching an electrical power circuit. Its primary purpose is to control large amounts of electrical power through its contacts, making it essential for applications like motor control and lighting systems. Contactors ensure safe and efficient switching operations in industrial and commercial settings.
Contactors are versatile devices used to control various electrical loads. They are commonly employed in applications such as motor starters, lighting control, heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, and other high-power switching operations. Their ability to handle high currents makes them ideal for industrial automation and control.
A power relay and a contactor serve similar functions but differ in their design and applications. Power relays are typically used for lower power applications and have fewer contacts. Contactors, on the other hand, are designed to handle higher currents and voltages, making them suitable for heavy-duty industrial applications. Additionally, contactors often include auxiliary contacts for added functionality.
The three main types of contactors are:
- Magnetic Contactors: Use an electromagnetic coil to close the contacts and control the electrical circuit.
- Mechanical Latching Contactors: Maintain their position without continuous power, using a mechanical latch.
- Solid-State Contactors: Use electronic components to switch the circuit, providing faster response times and longer lifespan without mechanical wear.
These types of contactors cater to different application needs, offering solutions for various industrial and commercial requirements.